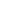

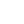
The Chase–Lloyd House is a historic house at 22 Maryland Avenue in Annapolis, Maryland. Built in 1769-1774, it is one of the first brick three-story Georgian mansions to be built in the Thirteen Colonies, and is one of the finest examples of the style. Its interiors were designed by William Buckland. Its construction was started for Samuel Chase, who would later be a signatory to the Declaration of Independence and Associate Justice of the Supreme Court, but Chase sold the building unfinished to Edward Lloyd IV in 1771. Lloyd completed the house in 1774 with assistance from Buckland and another architect, William Noke. The house remained in the Lloyd family until 1847, when it was sold back to descendants of Chase. In 1888 the house was bequeathed for use as a home for elderly women. It continues in this use today. While the upper floors are off limits to visitors, the main floor and the extensive gardens are open to the public.DescriptionThe three story brick house stands over a tall basement and measures 54ft wide and 43ft deep. The 18in thick walls are laid in Flemish bond with belt courses of rubbed brick at the second and third floor lines. The front is accented by a central three-bay wide projecting pavilion. The three-part central door with pediment, entablature, fanlight and sidelights is unusual for pre-Revolutionary times. Above the door a triple window on the second floor is followed by an arched window on the third floor. Windows are capped by flat arches of rubbed brick. First and second floor windows are six-over-six, while third floor windows are six-over-three. The rear pavilion features a large Palladian window that relates to the main stair landing on the interior.
 Hammond-Harwood House
40 meter
Wonderfully curated 18th-century manor house with all original architecture. Friendly...
Hammond-Harwood House
40 meter
Wonderfully curated 18th-century manor house with all original architecture. Friendly... William Paca House & Garden
180 meter
The Paca house is a wonderful place to visit. Mr. Paca was one of the 4 signers of t...
William Paca House & Garden
180 meter
The Paca house is a wonderful place to visit. Mr. Paca was one of the 4 signers of t... US Naval Academy Museum
243 meter
A small, interesting museum with a good amount of varied, US Naval artifacts. Highly ...
US Naval Academy Museum
243 meter
A small, interesting museum with a good amount of varied, US Naval artifacts. Highly ... Historic Annapolis, Inc.
244 meter
Historic Annapolis, Inc.
244 meter
 The Barracks
272 meter
The Barracks
272 meter
 Historic Annapolis Museum and Store
438 meter
It was nice to go up and experience the visual and audio learning upstairs, and to co...
Historic Annapolis Museum and Store
438 meter
It was nice to go up and experience the visual and audio learning upstairs, and to co... Banneker-Douglass Museum
575 meter
Small museum that does a great job introducing the long and continuing journey for Af...
Banneker-Douglass Museum
575 meter
Small museum that does a great job introducing the long and continuing journey for Af... Annapolis Maritime Museum
1 miles
This welcoming little museum greets you with a small free parking lot and a tiny outd...
Annapolis Maritime Museum
1 miles
This welcoming little museum greets you with a small free parking lot and a tiny outd... innerpotential.com
1 miles
innerpotential.com
1 miles
 The Chesapeake Children's Museum
1 miles
This is likely the least professional "children's museum" I have ever been in. The st...
The Chesapeake Children's Museum
1 miles
This is likely the least professional "children's museum" I have ever been in. The st... Jurassic park
2 miles
Jurassic park
2 miles
 Raven Maritime Studio
2 miles
Raven Maritime Studio
2 miles
 Perez Studio
3 miles
Perez Studio
3 miles
 National Cryptologic Museum
18 miles
Tricky to reach around the security, however that best set the tone for the topic. M...
National Cryptologic Museum
18 miles
Tricky to reach around the security, however that best set the tone for the topic. M...to add Chase Home map to your website;
We use cookies and other tracking technologies to improve your browsing experience on our website, to show you personalized content and targeted ads, to analyze our website traffic, and to understand where our visitors are coming from. Privacy Policy