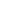

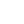
The Sterling Hill Mine, now known as the Sterling Hill Mine Tour & Museum of Fluorescence, is a former iron and zinc mine in Ogdensburg, Sussex County, New Jersey, United States. It was the last working underground mine in New Jersey when it closed in 1986. It became a museum in 1989. Along with the nearby Franklin Mine, it is known for its variety of minerals, especially the fluorescent varieties. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places on 1991.HistoryMining began at the site in the 1630s, when it was mistakenly thought to be a copper deposit. George III of the United Kingdom granted the property to William Alexander, titled Lord Stirling. Stirling sold it to Robert Ogden in 1765. It went through several owners until the various mines were combined into the New Jersey Zinc Company in 1897. The mine closed in 1986 due to a tax dispute with the town, which foreclosed for back taxes in 1989 and auctioned the property to Richard and Robert Hauck for $750,000. It opened as a museum in August 1990.GeologyThe ore bodies at the Sterling Hill mine lie within a formation called the Reading Prong massif; the ores are contained within the Franklin Marble. This was deposited as limestone in a Precambrian oceanic rift trough. It subsequently underwent extensive metamorphosis during the Grenville orogeny, approximately 1.15 billion years ago. Uplift and erosion during the late Mesozoic and the Tertiary exposed the ore bodies at the surface; the glaciers of the Pleistocene strewed trains of ore-bearing boulders for miles to the south, in places creating deposits large enough to be worked profitably.
 Franklin Mineral Museum Inc
2 miles
Unusual rocks and minerals. A great place to visit with children. Bringing a fluoresc...
Franklin Mineral Museum Inc
2 miles
Unusual rocks and minerals. A great place to visit with children. Bringing a fluoresc... Space Farms: Zoo & Museum
10 miles
The enclosures are extremely old and outdated. The animals have very little room to ...
Space Farms: Zoo & Museum
10 miles
The enclosures are extremely old and outdated. The animals have very little room to ... Snowmobile Barn Museum
14 miles
Amazing selection of historic snowmobiles, motorcycles, and other odd vehicles. Worth...
Snowmobile Barn Museum
14 miles
Amazing selection of historic snowmobiles, motorcycles, and other odd vehicles. Worth... The Stickley Museum at Craftsman Farms
17 miles
Very interesting! I had no idea Stickley lived in NJ. It's cool to find and learn loc...
The Stickley Museum at Craftsman Farms
17 miles
Very interesting! I had no idea Stickley lived in NJ. It's cool to find and learn loc... Whippany Railway Museum
20 miles
Nice selection of rolling stock. I was there when the museum was closed but they were...
Whippany Railway Museum
20 miles
Nice selection of rolling stock. I was there when the museum was closed but they were... Washington's Headquarters Museum
21 miles
Great trip for history buffs as well as those who should be! See the home Washington...
Washington's Headquarters Museum
21 miles
Great trip for history buffs as well as those who should be! See the home Washington... Macculloch Hall Historical Museum
21 miles
Local and national history mixed in one beautiful 17th century home, a must for any l...
Macculloch Hall Historical Museum
21 miles
Local and national history mixed in one beautiful 17th century home, a must for any l... Morris Museum
21 miles
Kids had fun. There was a chocolate exhibit going on. It's good for a few hours, but ...
Morris Museum
21 miles
Kids had fun. There was a chocolate exhibit going on. It's good for a few hours, but ... Imagine That!!!
23 miles
We had my daughter's second birthday party here! Our host Tony was absolutely amazing...
Imagine That!!!
23 miles
We had my daughter's second birthday party here! Our host Tony was absolutely amazing... American Labor Museum Inc
24 miles
This museum doesn't just represent a crucial era in labor history, but also reflects ...
American Labor Museum Inc
24 miles
This museum doesn't just represent a crucial era in labor history, but also reflects ... Grover Cleveland Birthplace Historic Site
24 miles
Nice historical home in a setting convenient to western Essex County, New Jersey. Th...
Grover Cleveland Birthplace Historic Site
24 miles
Nice historical home in a setting convenient to western Essex County, New Jersey. Th... Museum of Early Trades & Crafts
24 miles
I am not a huge fan of museums and most mueseums are about historical stuff. This mus...
Museum of Early Trades & Crafts
24 miles
I am not a huge fan of museums and most mueseums are about historical stuff. This mus... Paterson Museum
25 miles
This is definitely one of the best museums around. Surprising that it's free!
Paterson Museum
25 miles
This is definitely one of the best museums around. Surprising that it's free! Lambert Castle Museum
26 miles
Beautiful building and incredible views of the New York-New Jersey area.
Lambert Castle Museum
26 miles
Beautiful building and incredible views of the New York-New Jersey area. Yogi Berra Museum
26 miles
Great insight and artifacts from Yogi's life in baseball. Quite area, self directed &...
Yogi Berra Museum
26 miles
Great insight and artifacts from Yogi's life in baseball. Quite area, self directed &... Montclair Art Museum
27 miles
One of best place to have a day with family. kids love to have a art class with loca...
Montclair Art Museum
27 miles
One of best place to have a day with family. kids love to have a art class with loca... United States Golf Association
29 miles
What an excellent golf Museum and most impressive putting greens. Highly recommend st...
United States Golf Association
29 miles
What an excellent golf Museum and most impressive putting greens. Highly recommend st...to add Sterling Hill Mining Museum map to your website;
We use cookies and other tracking technologies to improve your browsing experience on our website, to show you personalized content and targeted ads, to analyze our website traffic, and to understand where our visitors are coming from. Privacy Policy